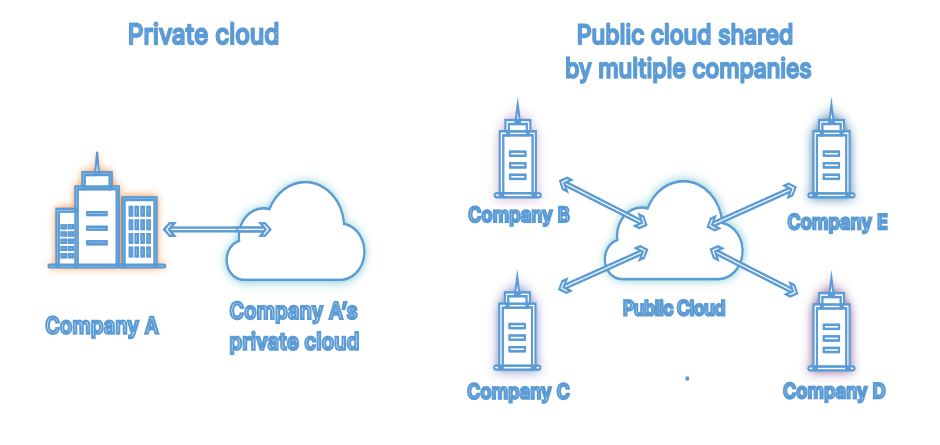
The key differences between public and private clouds lie in accessibility and ownership. Public clouds are like sharing a big building or public transportation bus, while private clouds are like having your special place or a car you brought just for you.
- Public Cloud: Share the sky, split the bill.
- Private Cloud: Your digital fortress, your rules.
Once you have made up your mind about opting for a cloud computing plan, the next big step involves deciding on the use of either a public cloud service, or the creation of a private cloud. Private versus public cloud is an issue that organizations wishing to maximize their IT assets have now come to face.
Each model presents distinct advantages and considerations that shape the digital landscape in which organisations operate. The decision hinges on security, scalability, control, and cost-effectiveness.
What are the Difference between Public and Private Cloud?
The primary difference between public and private clouds revolves around accessibility. Public clouds are shared among organizations, providing cost-effective scalability. In Contrast private clouds offer exclusive ownership for enhanced security and control. Consider your specific needs in scalability, control, and privacy when choosing between them.
This article explores the differences between private and public clouds, giving businesses a detailed analysis to help them choose wisely based on their specific needs. By understanding the details of these models, businesses can use cloud computing to boost their growth and efficiency.
Comparison: Public vs Private Cloud
| Aspect | Private Cloud | Public Cloud |
|---|---|---|
| Ownership | Dedicated to a single organization | Shared among multiple organizations |
| Control | Full control over infrastructure and settings | Limited control due to third-party management |
| Security | More secure due to dedicated nature | Robust security measures but shared resources |
What is a Public cloud?
In a public cloud arrangement, resources, as well as services, are supplied and administered by a third party, the Cloud Service Provider (CSP), to the users over the internet on a rental and pay per use basis in the form of platform as a service (PaaS), infrastructure as a service (IaaS) and software as a service (SaaS).
According to this model, the cloud host owns, supplies and manages all the resources (e, g, hardware, software and any other cloud-related gadgets), which are used by various users. To mention some of them: we have Amazon Web Services, Microsoft Azure and Google Cloud Platform.
They provide their services on multi-tenancy basis whereby a number of organizations or entities referred to as ‘Tenants’ can efficiently utilize the equally divided cloud hosting and computing resources like servers, storage, and other such resources.
What is a Private cloud?
A private cloud is a computing model where resources and infrastructure are utilized only by one single organization. A defining characteristic of a private cloud service is that it allows for more perforation, safety and personalization than in the case of various public cloud services.
In contrast to a public cloud solution where infrastructures are duplicated to serve several organizations, a private cloud is constructed and operated for one organization only. This isolation presents a perfect opportunity to government and financial institutions where there are stringent compliance barriers and even the nature of the information that gets disturbed is very sensitive.
Let us discuss some of the major advantages and disadvantages of Public and Private Cloud.
Public vs Private Cloud - Advantages & Disadvantages
Check out below for a simpler way to learn the advantages and disadvantages of the Public and Private cloud.
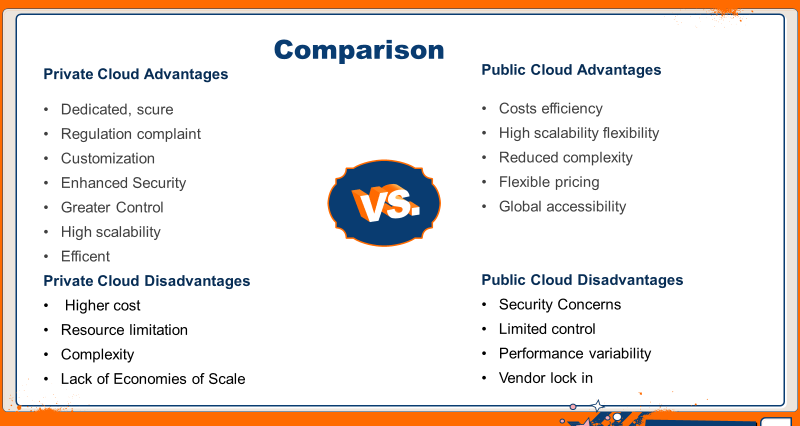
Advantages of Public Cloud
It’s quite normal to feel a little less willing to take the plunge into public cloud. But hey, there are some pretty cool things you might be missing out on the that if you’re sticking solely to on-premises or private cloud setups.
1. Cost Efficiency
Public cloud services offer on-demand payment options whereby users need not make any preliminary investments in hardware or other infrastructure. This cost-effective approach is ideal for new businesses as well as small businesses.
2. Scalability
Public clouds offer unparalleled scalability, allowing organisations to adjust resources up or down based on demand quickly. This flexibility is ideal for handling fluctuating workloads.
3. Minimal Maintenance
Public cloud service providers handle maintenance tasks, including hardware updates, security patches, and system monitoring. This frees up internal IT resources for strategic initiatives.
4. Global Accessibility
Public clouds enable users to access resources from anywhere via the Internet, facilitating remote work and collaboration.
5. Innovation and Speed
Public cloud providers often offer various services, tools, and APIs that enable rapid application development, testing, and deployment.
Disadvantages of Public Cloud
Although public cloud models are effective for numerous businesses, they entail several drawbacks, including:
1. Security Concerns
The use of shared resources with several users raises security issues such as loss of data and compliance as well. Organizations with stringent security requirements, however, may be reluctant to convert to the use of public cloud computing.
2. Limited Control
Organizations have limited control over the infrastructure and security measures in a public cloud. The cloud provider makes decisions about hardware and configurations.
3. Performance Variability
Performance can vary due to the shared nature of resources. During peak usage times, performance may degrade if other users consume significant resources.
4. Vendor Lock-In
Transitioning from one public cloud provider to another can be complex due to differences in services, APIs, and data formats. This can create a level of vendor lock-in.
5. Compliance Challenges
Public clouds may not be suitable for industries with stringent compliance requirements, as data storage and processing locations are not always under the organisation’s control.
Advantages of Private Cloud
The majority of benefits derived from a private cloud deployment model stem directly from your business’s capacity to independently control various aspects. These benefits include:
1. Enhanced Security
Private clouds offer heightened data security since they are isolated from external users. This makes them suitable for organisations dealing with sensitive information or compliance mandates.
2. Greater Control
Organizations have complete control over a private cloud’s infrastructure, resources, and configurations. This level of control allows for customisation to meet specific business needs.
3. Customization
Private clouds can be configured according to the needs of the organization which allows one to introduce certain necessary security measures, software or network configuration.
4. Predictable Performance
Since resources are not shared with other organisations, private clouds typically offer more predictable and consistent performance levels.
5. Compliance and Regulation
Niche industries such as healthcare or finance that are regulated from inside out can resort to the enhanced services provided by a private cloud reducing the risks of data violations.
Disadvantages of Private Cloud
Let see what are the Drawbacks of a Private Cloud Deployment Model
1. Higher Costs
Building and maintaining a private cloud involves significant upfront costs for hardware, software, and infrastructure. Ongoing maintenance and management can also contribute to higher operational expenses.
2. Resource Limitations
Private clouds have a finite amount of resources, which can become a limitation if an organisation needs growth.
3. Complexity
Setting up and managing a private cloud requires skilled IT personnel and expertise. This can lead to increased complexity and potential challenges in configuration and maintenance.
4. Scalability Challenges
Scaling a private cloud can be more complex and resource-intensive than public clouds, especially when sudden spikes in demand occur.
5. Lack of Economies of Scale
Private clouds do not benefit from the economies of scale that public clouds offer due to resource sharing among multiple organisations.
Public Cloud vs Private Cloud: Features
Important note: The primary distinction feature between private and public cloud computing revolves around their access.
| Feature | Public Cloud | Private Cloud |
|---|---|---|
| Infrastructure | Not private; shared among various organizations | Dedicated solely to the establishing organization |
| Sharing | Shared server or storage device | Exclusive hosting for data and applications |
| Billing | Based on usage (minutes to months) | Initial expenses for hardware and software deployment |
| Scalability | Quick setup for new servers | Available to a certain extent; additional hardware investment may be necessary |
| Ownership | Managed by the cloud provider | Managed by the organization |
Public Cloud - Features
- As the name suggests, the infrastructure isn’t private in a public cloud, unlike the private cloud.
- Various organisations share the same server or storage device in the public cloud.
- Public cloud providers bill to customers based on how long they use computing resources, which can range from minutes to months.
- When users need a new server, they can set one up quickly in the public cloud.
Private Cloud - Features
- Private cloud is dedicated solely to the organization that establishes it, ensuring exclusive hosting of data and applications and addressing security and privacy concerns.
- Scalability is available to a certain extent within a private cloud, although additional hardware investment may be necessary if demand surpasses available resources.
- Initial expenses for creating a private cloud encompass hardware and software deployment, with potential utilization of management software for billing various departments for cloud usage.
- In a typical private cloud arrangement, organizations undertake the procurement, setup, management, and maintenance of hardware and the associated data center.
Final words:
As the modern business landscape evolves, the choice between private vs public clouds emerges as a strategic crossroad that requires careful consideration. A private cloud is important because it provides a secure setting suitable for organizations that have high security and compliance requirements. In contrast, the public cloud has the greatest scalability and is affordable which explains the appeal for many who are interested in expansion.
Having looked into the differences and the merits as well as demerits of both models, it is clear that the choice depends on the specifics – priorities, resources, and needs of the organization. Whether harnessing the security of a private sanctuary or the limitless potential of the public expanse, aligning the cloud strategy with business goals is the compass that guides businesses toward success in the digital age.
FAQs: Private Cloud Versus Public Cloud
Public clouds are shared among organizations, offering cost-effective scalability. In contrast, private clouds provide exclusive ownership and control for heightened security and privacy.
The private cloud offers dedicated resources and enhanced security, while the public cloud provides scalability and cost savings. Ultimately, your choice between private and public cloud hinges on your organization's unique needs.
Cloud computing services provide different levels of abstraction and functionality, catering to various business needs and requirements. Includes
- Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS): Examples include Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform (GCP).
- Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS): Examples include Heroku, Microsoft Azure App Service, and Google App Engine.
- Software-as-a-Service (SaaS): Examples include Salesforce, Google Workspace (formerly G Suite), and Microsoft Office 365.
The primary difference between private and hybrid clouds is their setup and usage. Private clouds are dedicated environments used exclusively by a single organisation, offering enhanced control and security. The public cloud is like sharing the sky and splitting the bills
On the other hand, hybrid clouds combine private and public cloud resources, allowing data and applications to move seamlessly between them. Hybrid clouds offer flexibility and scalability, leveraging the benefits of both private and public clouds.
In a nutshell, cloud computing brings you all sorts of computer services over the internet, like servers, storage, and software. It's like having a virtual toolbox that lets you access what you need quickly and easily, allowing for faster innovation and saving you time and money.