You might still recall over the time when you’d constantly deal with complicated spreadsheets and wait for lengthy software updates while praying that your computer does not crash.
Rejoice! Those dark days are now a part of history. The advent of cloud computing and services like SaaS has made working with software as simple as scrolling through your social media feed. Now, you don’t have to worry about costly installations, intricate licensing procedures, and maintaining data centers or software houses.
When you get started with SaaS, you will have the option of paying only for the program that you need and then accessing it from anywhere. Imagine how relaxed you will feel as you manage money on your phone, communicate with people in real-time, and effortlessly conduct marketing campaigns.
This article will be your guide to learning about SaaS and looking at its benefits for organizations of all kinds. Let us move forward so you won’t have to wait long to optimize your workflow and boost your productivity!
What is Software as a Service or SaaS?
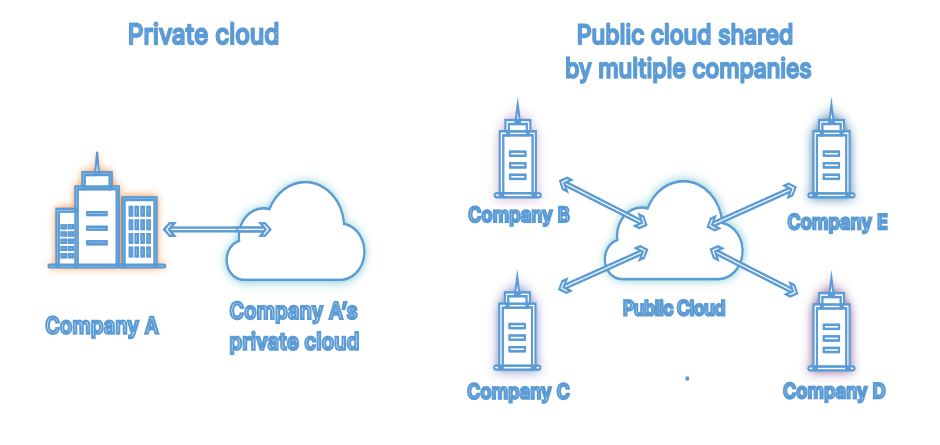
How does SaaS work?
SaaS uses a cloud-based distribution framework to operate. A software business or an independent vendor collaborates with them and then provides robust servers and storage on rent. All this happens in a distant data center referred to as the cloud.
This physical data center maintains the software program and all data associated with it, such as files and user accounts. The distinct benefit of SaaS is that you may access the program through a web browser on any device with an internet connection.
The good news is that there will not be any heavy installs or software upgrades to look after. This architecture makes sure that all users share the same core application, but everyone gets their allocated space for data and settings.
This approach saves the provider funds while also taking care of the fact that everyone gets the latest features at the same time. Data security is also an important consideration, with local or cloud-based storage solutions depending on your unique needs and regulatory requirements.
SaaS or Software as a Service is a software delivery system that uses the cloud. Using it, consumers can access their desired programs via the Internet instead of owning them altogether. Email, calendaring, and interactive applications such as Slack are all common SaaS examples.
SaaS is a shift from the conventional paradigm of software and computing. You won’t have to deal with time-consuming and lengthy installations and forego the IT intricacies that come with managing servers. You can just pay and subscribe for the software you need and then access it easily from any device.
This way SaaS becomes an excellent choice for all kinds of organizations, from individual entrepreneurs to multinational companies. It also offers you a wide range of applications that cover everything from personal demands to intricate commercial requirements.
The upcoming era might witness a revolution of software that is firmly based in the cloud. With SaaS, you do not just pay for software; you are also familiarized with a world of scalability, flexibility, and unlimited possibilities. Get ready to navigate the exciting universe of SaaS, unravel its benefits, and utilize it to enhance your personal and business productivity.
What kind of infrastructure does SaaS have?
SaaS apps work on a multi-tenant framework as far as the infrastructure is concerned. This means that the server of the supplier hosts a single version of the software program. This is used to serve all subscribing clients or tenants.
While all of these consumers are practically using the same fundamental application and setup, their data and files are stored separately to uphold privacy and maintain security.
This multitenant and collaborative strategy is highly beneficial and serves a long list of advantages. It gets simple to conduct repairs, bug fixes, and modifications since You will only execute them on one version of the application. Second, as the infrastructure is shared and used jointly by all of the tenants, there is an efficient utilization of resources.
In addition, the innovative design gives way to flexibility and scalability by allowing the service provider to cope with an expanding customer base without compromising fundamental features. In essence, the SaaS architecture provides a cost-effective solution to let you enjoy all perks of software applications.
What are some benefits of SaaS?
SaaS has multiple benefits over typical software acquisition. Here are some of the main benefits:
1. Reduced Expenses and Cost-effectivity
SaaS minimizes the burden of initial expenditures required for purchasing hardware, necessary software licensing, and technical assistance that you need when working on in-house applications. With SaaS, organizations just have to pay a membership fee, which makes budgeting simple to predict.
2. Flexible Payments
Contrary to conventional approaches where you have to purchase the software, SaaS lets you use payments based on subscription. This equates the operational expenditures throughout the process, which might help you use resources for other purposes. Consumers may also terminate their membership at any moment to avoid unnecessary fees.
3. Scalability and Adaptability
SaaS excels in providing scalability and flexibility. Businesses will be able to simply scale up or down depending on their requirements. You can also add or eliminate features according to your wishes.
4. Automatic Updates
The cloud-based provider, SaaS handles software upgrades and takes care of security protocols, allowing your IT personnel to focus on other duties.
5. Uninterrupted Accessibility
As SaaS apps are provided over the internet, users have the option to access them from practically anywhere with a reliable connection to the web and a suitable device.
6. Persistence
SaaS apps reside in the cloud making sure that your data is always available. Even if your location’s hardware fails, you won’t be deprived of the services
7. Customization
Most SaaS systems provide avenues for customization, adaptation, and integration with other business applications, specifically those from the same supplier.
What are the downsides of using SaaS?
While SaaS has immense advantages, it’s crucial to be aware of possible downsides before jumping in.
1. Vendor Dependability
Companies often outsource the requirements of their software to an external vendor. This entails relying on the vendor to maintain the program functioning, secure, and correct invoicing.
2. External Issues and Disruptions
Customers don’t have much influence over outside variables and they might affect service. These may include provider failures, unforeseen modifications to offering services, and even security issues. All of these aspects can create a big impact and impact your ability to utilize the program effectively.
3. Version Management Loss
Typically, SaaS providers look after the process of software versioning. A new version is allocated to every client notwithstanding their preferred choices. In order to get used to new features, your company might need additional training and effective resource allocation.
4. Limitation of Vendor Lock-in
Switching between different SaaS providers might be tough. Large data quantities must be transferred, and some suppliers’ proprietary technology impedes data transfer to other systems. This might result in vendor lock-in, making transferring to another supplier difficult and expensive.
5. Security Concerns
Cloud security is quite concerning for many companies thinking about opting for SaaS. Data held by an external server raises concerns about breaches of security and access control.
6. Limited Options for Customization
While some SaaS applications allow you to add modifications, the options may be relatively less as compared to software apps installed on-premises. This may limit the consumer’s ability to customize and modify the software according to your exact requirements.
7. Dependency on Internet
For SaaS programs to operate, you require a stable internet connection. Limited or erratic internet access can interrupt your workflow and lessen your productivity.
How does SaaS provide Security?
SaaS provides the easiest method to get access to quality software, but safety concerns may serve as an obstacle to some enterprises. Opposed to conventional software, where you are responsible for managing the security environment, SaaS security is a collaborative effort and requires efforts from each individual.
The cloud-based supplier keeps a check on the application code and the underlying infrastructure, while you focus on protecting your access credentials and passwords. While this kind of strategy has its advantages, there is always room for data privacy and security concerns to arise.
Data encryption remains a pertinent problem and can arise both during rest and in transit. To ensure that your data is protected, organizations should be confident that they have the potential to control encryption keys correctly.
In addition, strict access controls are needed to impede unauthorized individuals from getting your critical information and private data. This underlines the significance of Identity and Access Management (IAM) as an essential part of the SaaS platform.
If you wish to get rid of these issues, choose a renowned and reliable SaaS provider that contains strong security procedures. Look out for a service that can offer the best security monitoring, emergency response capabilities, and a trustworthy connection with your present security systems.
Furthermore, make a confirmation that the supplier follows all the data privacy standards and handles data in places that align with any applicable and relevant constraints. Finally, being open when communicating with the provider regarding their security procedures and potential dangers is also very important if you wish to establish confidence and maintain a safe SaaS experience.
What are the pricing tiers of SaaS?
SaaS pricing tiers are in a striking distinction from conventional software licensing. SaaS is frequently more affordable and cost-effective since it reduces the need for any hardware setup and maintenance procedures. But how will you choose the ideal pricing scheme available from SaaS providers? Here’s a list of some pricing plans of SaaS providers:
| Subscription Model | Description |
|---|---|
| Free Tier | Basic services are free but supported by advertisements. Upgrading to a paid tier removes ads. |
| Flat Rate | Services are billed at a pre-determined monthly or annual fee, ideal for predictable usage but not for minimal features. |
| Per User | Pricing is based on the number of users, with a set rate per user, adjustable according to team size. |
| Per User Tiers | A variation of the per-user model, offering different pricing plans for teams of varying sizes. |
| Storage Tiers | Basic services come with limited storage; additional storage requires a premium plan. |
| Pay-As-You-Go | Bills are based on usage, perfect for those with unpredictable usage patterns. |
| Per Active User | A combination of per-user and pay-as-you-go models, charging only for active users. |
| Feature-Based Tiers | Pricing varies based on features required. Basic versions are cheaper, while advanced versions unlock more features at a higher price. |
| Freemium | Offers a free, basic entry-level plan with limits, encouraging upgrades to premium tiers for advanced features. |
What are some vendors and examples of SaaS?
The SaaS industry is a thriving one and is flooding with suppliers and vendors of all sizes! From entrepreneurs starting their businesses to technological giants like Google, Microsoft, and Amazon, they’re all in a fight for your attention.
SaaS provides many applications and is not just confined to business processes.
You can sell SaaS solutions mostly to B2B, B2C, or both. Examples of some prominent SaaS products are:
- Salesforce
- HubSpot Trello
- Office 365
- Zoom
- Zendesk
- Netflix
- DocuSign and Slack
- Mailchimp
- Shopify
- Google Workspace Apps
- Adobe Creative Cloud
Conclusion: SaaS
In a nutshell, SaaS has caused a magical shift in the way we use software and develop programs. You will have nothing to worry about when you eliminate cumbersome installs and hefty licensing. SaaS provides a reliable and cost-effective approach to using sophisticated and innovative programs over the cloud.
You can benefit from automatic updates and multi-tenant design, making maintenance easier and resource allocation more efficient. Whether you’re just a start-up firm or a huge developed organization, there are several SaaS solutions out there available to meet your needs.
From the basic chores to industry-specific requirements and processes, everything is covered. So, now if you need software in the future, think about the flexibility and convenience that comes with SaaS – it’s like having a secure and evolving software suite right at your fingertips!