The Internet of Things (IoT) is a network of physical objects embedded with sensors, software, and technology that connects and shares data through the Internet to streamline tasks and increase efficiency.
The Internet of Things (IoT) is a network of devices that connect to the Internet and exchange data without human intervention. These devices can range from phones and sensors to appliances and equipment. It allows physical objects to communicate with each other and automate tasks, resulting in improved efficiency and better decision-making in various industries.
IoT is a technology that connects everyday objects and devices to the internet, allowing them to collect and use data to enhance our lives. This technology has a wide range of applications in sectors like smart homes, healthcare, agriculture, logistics, and more.
This article explores the top 10 applications of IoT and how it’s changing our homes, industries, cities, and daily routines. Join us to discover how IoT is reshaping the world around us in innovative ways.
Top 10 Common Applications of IoT 2024
The Internet of Things (IoT) has transformed numerous aspects of our lives, introducing connectivity and intelligence to everyday objects. Here are 10 widespread applications of IoT technology:
- Modernizing Agriculture.
- Smart Homes.
- Transforming Healthcare.
- Industrial Internet of Things.
- Retail Shops.
- Smart City.
- Wearables.
- Transportation and Logistics.
- Environmental Monitoring.
- Smart Grids.
1. Modernizing Agriculture

The Internet of Things (IoT) plays a crucial role in modernizing agriculture and enhancing productivity in several ways:
Precision Farming: IoT sensors embedded in fields collect data on soil moisture, temperature, humidity, and nutrient levels. This information helps farmers make informed decisions about irrigation, fertilization, and pest control, leading to optimized resource usage and improved crop yields.
Livestock Monitoring: IoT devices such as smart collars or ear tags track the health, location, and behavior of livestock in real time. Farmers can monitor parameters like body temperature, activity levels, and feeding habits, enabling early detection of diseases, improved breeding management, and enhanced animal welfare.
Automated Machinery: IoT-enabled farm machinery and equipment, equipped with sensors and GPS technology, can autonomously perform tasks such as planting, harvesting, and spraying pesticides. This automation increases operational efficiency, reduces labor costs, and minimizes human error.
Crop Monitoring and Management: Drones equipped with IoT sensors capture high-resolution images of crops, allowing farmers to monitor crop health, detect anomalies, and assess crop growth patterns. This data enables timely interventions, such as adjusting irrigation schedules or applying targeted treatments, to maximize crop productivity.
Supply Chain Optimization: IoT solutions track agricultural products’ movement and storage conditions throughout the supply chain. From farm to fork, sensors monitor factors like temperature, humidity, and storage conditions, ensuring product quality and safety while minimizing waste and losses. This real-time monitoring helps businesses make eco-friendly choices and promote a more sustainable supply chain.
Environmental Monitoring: IoT devices measure environmental parameters such as air quality, weather conditions, and water quality. This data helps farmers implement sustainable practices, mitigate environmental risks, and comply with regulations, promoting long-term environmental stewardship.
2. Smart Homes

The Internet of Things revolutionizes smart homes by connecting various devices and appliances to the Internet, enabling remote monitoring, control, and automation. Here’s how IoT enhances smart homes:
Home Automation: IoT-enabled devices such as smart thermostats, lights, locks, and security cameras can be controlled remotely via smartphone apps or voice commands. Homeowners can automate routines, such as adjusting temperature settings, turning on/off lights, or locking doors, enhancing convenience and energy efficiency.
Energy Management: IoT sensors monitor energy usage patterns and environmental conditions within the home. Smart thermostats optimize heating and cooling based on occupancy and preferences, leading to energy savings. Additionally, smart meters provide real-time insights into electricity consumption, enabling homeowners to make informed decisions to reduce energy costs.
Security and Surveillance: IoT-powered security systems include smart cameras, motion sensors, door/window sensors, and smart locks. These devices send alerts to homeowners’ smartphones in case of suspicious activities or unauthorized entry, allowing for timely responses and enhanced home security.
Environmental Monitoring: IoT sensors measure indoor air quality, temperature, humidity, and even air pollution levels. Smart air purifiers, humidifiers, and ventilation systems adjust settings automatically to maintain optimal indoor conditions for occupants’ comfort and health.
Appliance Management: IoT-connected appliances such as refrigerators, washing machines, and ovens offer remote monitoring and control features. Homeowners can receive notifications about appliance status, schedule operations, and even diagnose problems remotely, improving convenience and appliance longevity.
Personalized Experiences: IoT platforms use data analytics and artificial intelligence to learn users’ preferences and habits over time. By analyzing user behavior and environmental data, smart home systems can personalize settings and automate actions to better suit individual lifestyles and preferences.
Health and Wellness: IoT devices support health monitoring and wellness management within smart homes. Wearable devices, smart scales, and health trackers integrate with home IoT systems to provide real-time health data and insights, promoting healthier lifestyles and early detection of health issues.
3. Transforming Healthcare

The Internet of Things transforms healthcare by revolutionizing patient care, improving operational efficiency, and enabling innovative healthcare delivery models. Here’s how IoT is reshaping the healthcare industry:
Remote Patient Monitoring: IoT devices such as wearables, biosensors, and medical implants collect real-time health data from patients outside traditional clinical settings. Healthcare providers can remotely monitor patients’ vital signs, medication adherence, and disease progression, enabling early intervention and personalized treatment plans.
Telemedicine and Telehealth: IoT facilitates virtual consultations, remote diagnostics, and telemonitoring services, allowing patients to receive medical care and advice from healthcare professionals without needing in-person visits. Telemedicine platforms integrate IoT devices, video conferencing, and electronic health records (EHRs) to deliver convenient and accessible healthcare services to patients in remote or underserved areas.
Smart Hospitals and Healthcare Facilities: IoT technologies optimize hospital operations and enhance patient experiences by automating workflows, streamlining resource allocation, and improving asset management. Smart hospital solutions include IoT-enabled medical devices, patient tracking systems, and facility management systems, resulting in reduced waiting times, improved patient flow, and enhanced staff productivity.
Medication Management: IoT-enabled medication adherence systems monitor patients’ medication intake and send reminders or alerts to ensure timely dosing. Smart pill dispensers, medication tracking devices, and mobile apps help patients manage their medication regimens more effectively, reducing medication errors and improving treatment outcomes.
Chronic Disease Management: IoT solutions support the management of chronic conditions such as diabetes, hypertension, and respiratory diseases by continuously monitoring patients’ health metrics and providing personalized interventions. Remote monitoring of vital signs, medication adherence, and lifestyle factors empowers patients to manage their chronic conditions and avoid exacerbations.
Predictive Analytics and Preventive Care: IoT data analytics tools analyze large volumes of healthcare data generated by IoT devices to identify patterns, trends, and predictive insights. Healthcare providers can use these insights to anticipate patient needs, detect early warning signs of disease, and implement preventive interventions to reduce hospital admissions and healthcare costs.
Enhanced Patient Engagement: IoT-enabled patient engagement platforms deliver personalized health education, coaching, and behavioral interventions to empower patients to take an active role in managing their health. Connected health apps, wearable devices, and patient portals facilitate communication between patients and providers, fostering greater engagement and collaboration in care delivery.
4. Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT)

The Internet of Things is transforming industries by providing connectivity, automation, and data-driven insights to improve operational efficiency, enhance decision-making, and drive innovation. Here are several ways IoT is helping industries:
Enhanced Operational Efficiency: IoT-enabled sensors, devices, and equipment collect real-time data on machinery performance, energy consumption, and production processes. By analyzing this data, industries can optimize operations, reduce downtime, and improve resource utilization, leading to increased productivity and cost savings.
Predictive Maintenance: IoT enables predictive maintenance by monitoring equipment health and performance metrics in real time. By analyzing sensor data for signs of wear, damage, or malfunction, industries can identify potential issues before they occur, schedule maintenance proactively, and prevent costly unplanned downtime.
Supply Chain Optimization: IoT facilitates supply chain visibility and optimization by tracking the movement, location, and condition of goods throughout the supply chain. Industries can use IoT-enabled tracking devices and logistics platforms to monitor inventory levels, streamline logistics operations, and improve inventory management, resulting in faster delivery times and reduced costs.
Quality Control and Assurance: IoT sensors and monitoring devices can track product quality and environmental conditions throughout the manufacturing process. By collecting data on parameters such as temperature, humidity, and pressure, industries can ensure product quality, compliance with regulatory standards, and customer satisfaction.
Safety and Security: IoT enhances workplace safety and security by monitoring environmental conditions, detecting safety hazards, and providing real-time alerts in hazardous environments. Industries can deploy IoT-enabled safety devices, wearables, and surveillance systems to prevent accidents, ensure compliance with safety regulations, and protect workers and assets.
Energy Management: IoT enables energy monitoring, optimization, and conservation in industrial facilities. By deploying IoT sensors and smart meters, industries can track energy consumption, identify areas of inefficiency, and implement energy-saving measures to reduce costs, minimize environmental impact, and achieve sustainability goals.
Asset Tracking and Management: IoT enables asset tracking and management by tagging and monitoring equipment, vehicles, and inventory in real time. Industries can use IoT-enabled asset tracking systems to optimize asset utilization, prevent loss or theft, and improve asset maintenance and lifecycle management.
Customer Experience Enhancement: IoT enables industries to deliver personalized and immersive customer experiences through connected products, services, and environments. By leveraging IoT-enabled devices and applications, industries can engage customers, gather feedback, and tailor products and services to meet their needs and preferences.
5. Smart Retail Shops

The Internet of Things, plays a significant role in revolutionizing retail shops by enhancing operational efficiency, improving customer experiences, and enabling data-driven decision-making. Here’s how IoT helps in retail shops:
Inventory Management: IoT sensors and RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) tags enable real-time tracking of inventory levels, item locations, and stock movement within retail stores. By automating inventory management processes, retailers can optimize stock levels, reduce out-of-stock situations, and minimize overstocking, leading to improved sales and customer satisfaction.
Shelf Monitoring and Product Placement: IoT-enabled smart shelves equipped with sensors can detect product movement, monitor shelf stock levels, and trigger automatic replenishment orders when items are running low. Retailers can use data analytics to optimize product placement, enhance merchandising strategies, and increase sales by ensuring that popular items are prominently displayed and readily available to customers.
Customer Analytics: IoT devices such as beacons and sensors collect data on customer foot traffic, dwell times, and browsing behaviors within retail stores. By analyzing this data, retailers can gain insights into customer preferences, shopping patterns, and demographic profiles, allowing them to personalize marketing messages, tailor product offerings, and improve store layouts to enhance the overall customer experience.
Omni-channel Integration: IoT enables seamless integration between physical retail stores and online channels, creating a unified omni-channel shopping experience for customers. Retailers can leverage IoT technology to offer click-and-collect services, enable in-store pickup of online orders, and provide real-time inventory visibility across all channels, allowing customers to shop anytime, anywhere, and through their preferred channels.
Smart Checkout Systems: IoT-powered checkout systems, such as self-service kiosks and mobile payment terminals, streamline the checkout process and reduce waiting times for customers. Retailers can implement IoT-based payment solutions, including contactless payments and mobile wallets, to offer convenient and secure payment options, improving customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Enhanced Security and Loss Prevention: IoT-based security systems, including video surveillance cameras, motion sensors, and access control devices, help retailers monitor store premises, deter theft, and prevent shrinkage. Real-time alerts and notifications enable immediate response to security incidents, ensuring the safety of customers, employees, and assets, while also reducing losses due to theft or vandalism.
Energy Management: IoT-enabled smart lighting, heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems help retailers optimize energy consumption, reduce utility costs, and minimize environmental impact. Automated energy management solutions adjust lighting and climate control settings based on occupancy levels, time of day, and weather conditions, maximizing energy efficiency without compromising comfort or safety.
6. Smart City

The Internet of Things, plays a crucial role in transforming cities into smart cities by leveraging technology to enhance urban infrastructure, improve public services, and promote sustainability and livability. Here’s how IoT helps in building smart cities:
Efficient Urban Mobility: IoT-enabled transportation systems, such as smart traffic lights, vehicle sensors, and intelligent parking solutions, optimize traffic flow, reduce congestion, and minimize travel times. Real-time traffic data and predictive analytics enable authorities to manage traffic patterns, improve public transportation routes, and enhance overall urban mobility for residents and commuters.
Enhanced Public Safety: IoT-based security and surveillance systems, including video cameras, gunshot detectors, and emergency response sensors, enhance public safety and law enforcement capabilities in smart cities. Integrated command centers receive real-time alerts and monitor critical incidents, enabling faster emergency response, crime prevention, and disaster management efforts to ensure the safety and security of citizens.
Sustainable Resource Management: IoT sensors and smart meters monitor and manage essential resources such as water, energy, and waste in smart cities. Automated systems detect leaks, optimize water usage, and reduce water wastage, contributing to water conservation and environmental sustainability. Similarly, IoT-enabled energy grids and smart buildings improve energy efficiency, reduce carbon emissions, and promote renewable energy adoption, supporting the transition to a greener and more sustainable urban environment.
Urban Environmental Monitoring: IoT sensors measure air quality, noise levels, and environmental pollutants in smart cities to monitor urban environmental conditions and protect public health. Real-time data analytics provide insights into environmental trends, identify pollution hotspots, and support proactive measures to mitigate environmental risks and improve air quality, ensuring a healthier and more livable urban environment for residents.
Smart Infrastructure Management: IoT-enabled infrastructure monitoring systems, such as smart bridges, roads, and utilities, detect structural defects, assess maintenance needs, and optimize asset performance in real-time. Predictive maintenance and asset management solutions minimize downtime, extend infrastructure lifespan, and enhance resilience against natural disasters and extreme weather events, ensuring the reliability and safety of critical urban infrastructure.
Citizen Engagement and Participation: IoT technology enables citizens to actively engage with city authorities, share feedback, and participate in decision-making processes to shape the future of their communities. Digital platforms, mobile applications, and IoT-enabled sensors facilitate communication, collaboration, and co-creation initiatives between government agencies, residents, and businesses, fostering a more inclusive and participatory governance model in smart cities.
7. Wearables
The Internet of Things plays a significant role in enhancing the functionality and capabilities of wearables, such as smartwatches, fitness trackers, and health monitoring devices. Here’s how IoT helps wearables:
Seamless Connectivity: IoT enables wearables to connect seamlessly to other devices, networks, and cloud-based platforms, facilitating data exchange and synchronization. Wearables can communicate with smartphones, tablets, and IoT-enabled devices to access information, receive updates, and transmit data in real time, ensuring a smooth and integrated user experience.
Remote Monitoring and Tracking: IoT-enabled wearables equipped with sensors and connectivity capabilities can monitor various health metrics, such as heart rate, sleep patterns, activity levels, and vital signs. Users can track their fitness goals, monitor their health status, and receive personalized insights and recommendations based on real-time data collected by the wearables. Healthcare providers can remotely monitor patients’ health conditions, detect abnormalities, and intervene proactively, improving patient outcomes and reducing healthcare costs.
Health and Fitness Coaching: IoT-powered wearables offer personalized health and fitness coaching based on user preferences, goals, and performance metrics. Wearables can analyze data trends, provide actionable insights, and offer motivational prompts to encourage users to adopt healthier habits, achieve fitness targets, and maintain an active lifestyle. Integration with fitness apps, social networks, and online communities enables users to share achievements, compete with friends, and stay motivated on their wellness journey.
Emergency Assistance and Safety: IoT-enabled wearables feature built-in emergency response capabilities, such as SOS alerts, fall detection, and location tracking, to ensure users’ safety and well-being. In case of emergencies or accidents, wearables can automatically notify designated contacts, emergency services, or caregivers, providing peace of mind to users and their loved ones. Wearables equipped with GPS, NFC, or cellular connectivity can transmit location data and facilitate quick rescue and assistance operations, especially in remote or hazardous environments.
Smart Home Integration: IoT-enabled wearables can serve as remote controls or interfaces for smart home devices and systems, allowing users to manage and control various home automation features, such as lighting, thermostats, security cameras, and appliances, directly from their wrists or wearable devices. Integration with smart home platforms, voice assistants, and IoT hubs enables seamless interaction and interoperability between wearables and connected home devices, enhancing convenience, comfort, and energy efficiency for users.
Contextual Awareness and Personalization: IoT-powered wearables leverage contextual data, such as location, time, weather, and user behavior, to deliver personalized experiences and services tailored to individual preferences and needs. Wearables can adapt their functionality, display content, and provide recommendations based on situational context, user habits, and environmental factors, enhancing usability, relevance, and user satisfaction.
8. Transportation and Logistics

The Internet of Things plays a pivotal role in revolutionizing transportation and logistics industries by offering innovative solutions to improve efficiency, safety, and sustainability across various aspects of the supply chain and mobility ecosystem. Here’s how IoT helps in transportation and logistics:
Fleet Management: IoT enables real-time monitoring and management of fleets, including trucks, ships, trains, and airplanes. Connected sensors and telematics devices installed in vehicles collect data on location, speed, fuel consumption, engine health, and driver behavior. Fleet managers can track vehicle performance, optimize routes, schedule maintenance, and ensure compliance with regulations, leading to reduced operational costs, enhanced productivity, and better resource allocation.
Asset Tracking and Inventory Management: IoT-powered tracking devices and RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) tags enable precise location tracking and monitoring of goods, packages, containers, and equipment throughout the supply chain. By providing real-time visibility into inventory levels, shipment status, and asset utilization, IoT facilitates efficient inventory management, reduces loss or theft, minimizes stockouts, and streamlines order fulfillment processes, improving overall supply chain efficiency and customer satisfaction.
Predictive Maintenance: IoT sensors embedded in vehicles, machinery, and infrastructure components enable predictive maintenance by continuously monitoring equipment condition, performance metrics, and environmental factors. Advanced analytics and machine learning algorithms analyze sensor data to predict potential failures, identify maintenance needs, and schedule proactive repairs or replacements before critical issues arise. Predictive maintenance reduces downtime, extends asset lifespan, and prevents costly disruptions, enhancing operational reliability and asset utilization.
Smart Traffic Management: IoT-powered traffic management systems leverage connected sensors, cameras, and intelligent algorithms to monitor traffic flow, detect congestion, and optimize signal timing in real-time. By collecting and analyzing traffic data, such as vehicle counts, speed, and occupancy rates, smart traffic systems can dynamically adjust signal phasing, prioritize emergency vehicles, and manage traffic flow to reduce congestion, alleviate bottlenecks, and improve road safety and efficiency.
Supply Chain Visibility and Optimization: IoT enables end-to-end visibility and traceability across the supply chain by integrating data from various sources, including suppliers, manufacturers, distributors, and retailers. By tracking goods’ movement, storage conditions, and handling processes in real-time, IoT facilitates supply chain optimization, demand forecasting, and inventory optimization. Enhanced visibility enables stakeholders to make data-driven decisions, improve collaboration, and respond quickly to changing market demands, enhancing supply chain resilience and agility.
Environmental Monitoring and Compliance: IoT sensors and monitoring devices enable real-time environmental monitoring and compliance management in transportation and logistics operations. By measuring parameters such as air quality, temperature, humidity, and noise levels, IoT helps identify environmental risks, assess regulatory compliance, and mitigate environmental impacts. IoT solutions support sustainability initiatives, reduce emissions, and enhance environmental stewardship across the transportation and logistics sector.
9. Environmental Monitoring

The Internet of Things plays a significant role in environmental monitoring by leveraging sensor technology and connectivity to collect real-time data on various environmental parameters. Here’s how IoT helps in environmental monitoring:
Air Quality Monitoring: IoT devices equipped with air quality sensors measure pollutants such as particulate matter (PM), nitrogen dioxide (NO2), sulfur dioxide (SO2), carbon monoxide (CO), and ozone (O3) in the atmosphere. These sensors are deployed across urban areas, industrial sites, and transportation hubs to monitor air quality levels and detect pollution hotspots. Real-time data collected from IoT devices enable authorities to assess air quality, identify sources of pollution, and implement targeted mitigation measures to improve public health and reduce environmental impact.
Water Quality Monitoring: IoT sensors are deployed in rivers, lakes, reservoirs, and coastal areas to monitor water quality parameters such as pH, dissolved oxygen (DO), temperature, turbidity, conductivity, and nutrient levels. These sensors continuously monitor water bodies and detect changes in water quality, pollution incidents, and harmful algal blooms. Real-time water quality data generated by IoT devices help authorities manage water resources, safeguard aquatic ecosystems, and ensure safe drinking water supplies for communities.
Soil Monitoring: IoT-enabled soil sensors are deployed in agricultural fields, forests, and natural habitats to monitor soil moisture, temperature, pH, nutrient levels, and salinity. These sensors provide valuable insights into soil health, moisture content, and fertility, enabling farmers, land managers, and environmental scientists to optimize irrigation, fertilizer application, and land use practices. Real-time soil data collected by IoT devices support precision agriculture, sustainable land management, and ecosystem restoration efforts.
Weather Monitoring: IoT weather stations equipped with sensors for measuring temperature, humidity, barometric pressure, wind speed, and precipitation are deployed across geographic regions to monitor weather conditions and forecast meteorological events. These weather stations provide essential data for weather prediction, disaster preparedness, and climate monitoring. Real-time weather data collected by IoT devices support early warning systems for severe weather events, agricultural planning, and climate change research.
Wildlife Monitoring: IoT-enabled wildlife tracking devices equipped with GPS, accelerometers, and environmental sensors are deployed to monitor animal behavior, movement patterns, and habitat usage. These devices enable researchers, conservationists, and wildlife managers to study wildlife populations, track endangered species, and assess the impact of human activities on biodiversity. Real-time data collected by IoT devices support wildlife conservation efforts, habitat restoration projects, and ecosystem management initiatives.
Disaster Monitoring and Early Warning: IoT-based monitoring systems are deployed in disaster-prone areas to detect natural hazards such as earthquakes, tsunamis, floods, landslides, and wildfires. These monitoring systems utilize sensors, cameras, and satellite imagery to detect anomalies, assess risk levels, and issue early warnings to communities at risk. Real-time data collected by IoT devices support disaster preparedness, emergency response, and recovery efforts, helping to save lives and minimize property damage during natural disasters.
10. Smart Grids
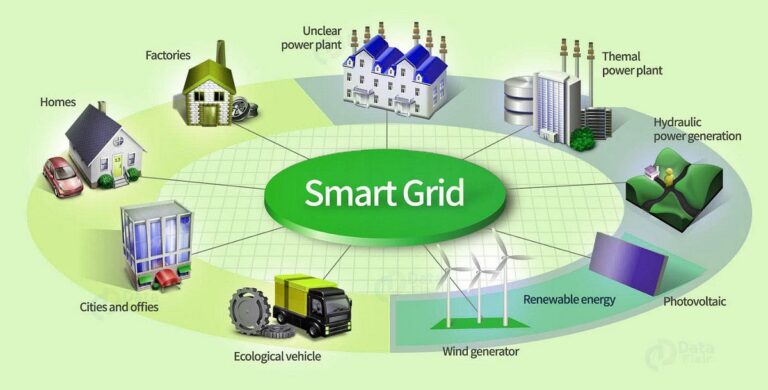
The Internet of Things plays a crucial role in transforming traditional power grids into smart grids by enabling advanced monitoring, control, and optimization of energy generation, distribution, and consumption. Here’s how IoT helps smart grids:
Remote Monitoring and Management: IoT sensors and devices are deployed across the power grid infrastructure to collect real-time data on energy generation, transmission, and distribution. These sensors monitor parameters such as voltage, current, frequency, and power quality at various points in the grid. Remote monitoring allows utilities to detect anomalies, identify faults, and proactively address issues to ensure grid reliability and stability.
Grid Optimization and Demand Response: IoT enables utilities to optimize grid operations and balance supply and demand in real-time through demand response programs. Smart meters and IoT-enabled devices installed in homes and businesses provide insights into energy consumption patterns and enable dynamic pricing schemes. Utilities can remotely adjust electricity tariffs based on demand fluctuations, incentivize energy conservation during peak periods, and mitigate grid congestion by shifting loads to off-peak hours, thereby optimizing grid performance and reducing energy costs.
Distributed Energy Resource Integration: IoT facilitates the integration and management of distributed energy resources (DERs) such as solar panels, wind turbines, energy storage systems, and electric vehicles (EVs) into the grid. IoT-enabled DERs communicate with grid operators and adjust their output based on grid conditions and energy market signals. This bidirectional communication enables utilities to harness renewable energy sources efficiently, balance supply and demand, and enhance grid resilience by integrating decentralized generation and storage assets.
Predictive Maintenance and Asset Management: IoT enables predictive maintenance of grid infrastructure by monitoring the health and performance of critical assets such as transformers, substations, and distribution lines. Sensors embedded in equipment detect anomalies, predict potential failures, and trigger maintenance alerts before equipment breakdowns occur. By adopting proactive maintenance strategies, utilities can minimize downtime, extend asset lifespan, and optimize maintenance schedules, leading to cost savings and improved reliability.
Grid Security and Resilience: IoT enhances grid security and resilience by detecting and mitigating cybersecurity threats and physical vulnerabilities. Cyber-physical systems equipped with IoT sensors monitor network traffic, detect anomalies, and identify potential cyberattacks or intrusions in real-time. Additionally, IoT-enabled grid components support self-healing capabilities by automatically isolating and rerouting power flows to prevent cascading failures and blackouts, thereby enhancing grid resilience and reliability in the face of disruptions or emergencies.
Data Analytics and Decision Support: IoT generates vast amounts of data from grid sensors, meters, and devices, which can be analyzed using advanced analytics and machine learning algorithms to derive actionable insights. Utilities can leverage data analytics to optimize grid operations, forecast energy demand, improve load forecasting accuracy, and optimize asset utilization. Decision support systems powered by IoT data enable utilities to make informed decisions, optimize resource allocation, and plan infrastructure investments effectively, driving operational efficiency and cost-effectiveness in smart grid management.
The latest “State of IoT – Spring 2024″ report, which is 148 pages long, confirms that IoT is still among the top three priorities for corporate technology. Although AI has surpassed IoT in corporate prioritization, the combination of IoT and AI is gaining momentum and is considered to be a positive force for the $236 billion IoT market, rather than a disruptor.
The global market for Artificial Intelligence (AI) in the Internet of Things (IoT) was valued at $3,808.5 million in 2024. It is predicted to grow significantly, reaching $10,280 million by 2032. This growth is expected to occur at a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 14.7% during the forecast period from 2024 to 2032. Interestingly, the AI industry is being led by both China and the United States, who are driving innovation and advancements in this rapidly evolving field.
This proliferation of IoT solutions can be attributed to several factors:
- Connectivity Advancements: The widespread availability of high-speed internet and advancements in wireless communication technologies like 5G have facilitated seamless connectivity between devices, making it easier to deploy and manage IoT solutions.
- Cost Reduction: The decreasing cost of IoT hardware components, such as sensors and microcontrollers, has made it more affordable for businesses to implement IoT solutions on a large scale.
- Data Analytics Capabilities: IoT devices generate vast amounts of data, and advancements in data analytics tools and techniques have made it possible to derive valuable insights from this data, driving business intelligence and decision-making.
- Improved Efficiency and Productivity: IoT solutions enable automation and remote monitoring of processes, leading to improved efficiency, reduced downtime, and increased productivity across various industries.
- Enhanced Customer Experience: IoT-enabled products and services can provide personalized experiences to customers by offering real-time insights, predictive maintenance, and customized recommendations based on user preferences and behavior.
- Industry Standards and Interoperability: The development of industry standards and protocols has facilitated interoperability between different IoT devices and platforms, enabling seamless integration and collaboration across ecosystems.
- Security and Privacy Measures: As IoT adoption grows, there is an increasing focus on implementing robust security and privacy measures to protect sensitive data and prevent unauthorized access, addressing concerns around cybersecurity.
Conclusion
The Internet of Things has diverse applications across various industries, ranging from smart homes and healthcare to agriculture and transportation, driving innovation, efficiency, and convenience. As IoT technologies continue to evolve, their impact on society and the economy is expected to grow significantly.
FAQs IoT (application)
IoT is used in various sectors, including smart home automation, industrial monitoring, healthcare wearables, agriculture, smart cities, retail, transportation, energy management, environmental monitoring, and asset tracking.
IoT enables remote patient monitoring, personalized medicine, real-time health data tracking, and improved healthcare delivery, leading to better patient outcomes, reduced costs, and enhanced efficiency.
In agriculture, IoT is used for precision farming, monitoring crop conditions, optimizing irrigation and fertilization, tracking livestock health, and predicting weather patterns, resulting in increased yields, resource efficiency, and sustainability.
IoT technologies in smart cities improve urban infrastructure, enhance public services like transportation and waste management, increase energy efficiency, promote environmental sustainability, and enhance overall quality of life for residents.
IoT enables monitoring and optimization of energy consumption in buildings, factories, and utilities, facilitates demand response programs, integrates renewable energy sources, and promotes energy conservation and sustainability.
IoT enables real-time tracking and management of assets such as equipment, vehicles, and inventory, improving asset utilization, security, and maintenance, and reducing operational costs.