Let’s explore the Future with 6G Network: which will be Faster, Smarter, and More Connected”
In telecommunications, wireless communication technology never fails to shock as just when we felt comfy with 5G as the best, debates have already commenced about its successor 6G (6th Generation). However, even though it is a work in progress fully conceived, the term ”sixth generation” has begun to surface leaving people enthralled as to what more will be
The new 6th generation technology coming soon is going to change everything. It will let us connect instantly from anywhere, way faster than what we have now with 5G. This means we’ll be able to do things we can’t even imagine yet. Wireless companies are already working on it, getting ready to bring us even better ways to stay connected and do things online.
In this blog, we’ll find out what exactly sixth generation is, how it’s different from what we have now, its features when it is coming, and what companies are working on it
What is 6G network Technology?
A sixth-generation network is referred to as the cellular mobile system that comes after the 5G system that enhances this mobile system with faster speeds, better latency, and advanced features that could positively change of several things within our lives.
In contrast to its current 5G counterpart, which is further viewed as the bearers of the next generation mobile system, 6G technology is anticipated to facilitate instantaneous connection in most place and at several multiples of the speed enjoyed with 5G networks today. It is anticipated that breakthroughs in technology employing terahertz frequencies, smarter antennas, and artificial intelligence will be incorporated.
It is also likely to be significantly faster and have speeds up to 100 times over that of 5G and allow a greater number of devices to be connected at the same time.
Transaction delays and any other geographical limitations that you have been experiencing will be resolved with the introduction of 6G networks Furthermore, it will also be possible to use the phone through multiple connections by linking various mobile devices to one contract. They’ll also bring cool new features like holographic communication, making it easier for our phones to work with artificial intelligence.
6G: The next horizon
6G on the Horizon: The Next Wave of Supercharged Connectivity and Smart Tech Advancements”
- 5G is just getting started, but 6G technology is already on the horizon, moving forward rapidly.
- Currently, telecom services gather data from networks, use AI to process it externally, and then manually adjust the network based on the findings.
- With the sixth generation networks are anticipated to autonomously make decisions at every level, eliminating the need for manual adjustments.
- 6G promises lightning-fast data transfers without buffering, lags, or dropouts, revolutionizing connectivity.
- Similar to how 2G introduced texting and 4G brought mobile apps, 6G will advance machine-to-machine communication, fostering seamless collaboration among smart devices.
Let’s Hear from Technology Leaders About 6G:
- Shamik Mishra: The Chief Technology Officer of connectivity within Capgemini Engineering explains that the deployment of 6G will bring forth devices such as networked vehicles, smart factories, and various forms of virtual and augmented reality.
- Swarun Kumar: An assistant professor at Carnegie Mellon University explains that 6G will contribute to improved public safety, health monitoring systems, and facial recognition technologies..
- Elon Musk: “6G is going to be perfect, it’s going to be a leap and change what we have not imagined” (Source: Musk, Elon. Twitter. January 5, 2023.
- Satya Nadella (CEO of Microsoft): “The promise of 6G is beyond enhancement, we see breakthrough opportunities in many industries.” (Source: Nadella, Satya. Keynote Speech at Mobile World Congress. March 15, 2023.
- Tim Cook (CEO of Apple): “6G will transform human-computer interaction, imbuing a new scope of technology and art as we know it.” (Source: Cook, Tim. Interview with Bloomberg. April 20, 2023.
- Jack Ma (co – founder of Alibaba Group): “6G can change the world for the better, and where it is used, all businesses will be effectively equipped.” (Source: Ma, Jack. Keynote Address at World Economic Forum. January 30, 2023.
How 6G will work?
It is true that to this date, no single country or organization has been able to sculpt a full picture of how all of these new technologies will function since the specifications are still being worked out by the International Telecommunication Union. However, knowing all achievements from cellular technologies and their range of operation, therefore, one can pinpoint some functions which the sixth generation is likely to develop.
1. Using Unused Spectrum:
Engineers are looking into using high frequencies for 6G, way beyond what 5G uses. There’s a lot of unused spectrum in these high frequencies that could let us transfer data super-fast.
2. Making Spectrum Use More Efficient:
Right now, wireless devices can either send or receive data on a certain frequency at one time. 6G might be able to improve this by using fancy math to send and receive data on the same frequency at the same time, making things faster and more efficient.
3. Mesh Networking:
Instead of just connecting to cell towers like in 5G, 6G might let devices act like mini cell towers themselves. This means devices could help each other out to expand coverage and make the network stronger.
4. Using a New Kind of Internet Protocol (IP):
There’s talk of 6G using a new version of the Internet Protocol (IP) to move data around. This new IP would be like a super-fast delivery service for data, making things even quicker and more reliable.
5. Smart Use of Frequencies:
6th generation will be smart about which frequencies it uses, adjusting wavelengths to avoid interference. This is based on the idea that different materials absorb and emit electromagnetic radiation at specific wavelengths, so 6G will take advantage of that to make sure signals get through without any problems.
Key Features of 6G
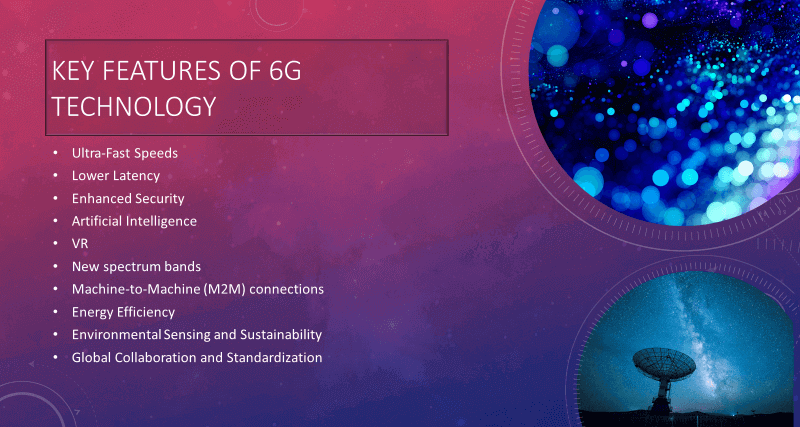
The actual implementation and features of sixth generation networks will depend on technological advancements, regulatory decisions, and market demands as they evolve. Here are Key features of potential direction for 6g technology.
1. Increased Data Rates:
The one aspect that many people cannot wait to appreciate with the 6th generation is speed. While 5G stands at a maximum of 20gb/s 6G is predicted to shoot up to 1tb/s. Now that is something else! Sixth-generation networks will enhance data rates several times higher than 5G owing to the growth of e-band technology.
This might imply a multi-terabit per second data transmission speed, making it possible to stream excessively high-definition videos, implement virtual reality technologies, and deploy massive internet of things.
2. Ultra-Low Latency:
One of the objectives of 6G is ultra-reliable low-latency communication, possibly around sub-millisecond latency. This will be important in use cases that require high reliability and timeliness as in cases of remote surgery, driverless cars, and interactive entertainment.
3. Spectrum Exploitation:
6th generation is believed to cover the frequencies above 100 GHz including terahertz band. This higher frequency band provides large spectral bandwidths however there are prominent engineering issues related to management of propagation and hardware construction.
4. AI Integration:
There is an anticipation of the use of artificial intelligence (AI) in the monitoring and optimization of 6G networks. Artificial intelligence could also be used to manage interference, predict failures, and allocate network resources.
5. Holographic Communication:
6G will bring an improvement in remote connection by allowing communication and interaction through 3 dimensional figures in real time. This may disrupt telepresence and collaboration and entertainment activities.
6. Quantum Communication:
Given the growing interest in quantum computing and communication, it is likely that 6G networks will embrace some quantum components. Communication will be made highly secure through the use of quantum transmission making it almost impossible to hack.
7. Energy Efficiency:
Compared to other previous generations, 6G is anticipated to utilize networks that are more energy efficient. This will be brought about by superior hardware configuration and the architecture of the network and management of power.
8. Environmental Sensing and Sustainability:
With the development of 6G, environmental sensing capabilities will also be integrated. For instance, air quality, temperature, pollution level and other parameters may be monitored. The collected information may be used relief application, climate monitoring etc.
9. Global Collaboration and Standardization:
As it was the case with other generations of wireless technology, the realization of the 6th generation development will also emmulate the global standardization and collaboration paradigm in order to make it have effective usage everywhere.
It has to be said once again that although those are reasonable ways in which this technology might evolve, what really matters will be the technological evolution, the regulations which will be adopted or evolved and the market that will develop as well over time.
Potential applications of 6G
The ramifications of 6G touches on several industries and sectors, thus providing opportunities for new developments, efficiency gains, and improved living standards.
Here’s the information organized into a table format:
| Potential Applications of 6G | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Enhanced Connectivity | 6G is more efficient and faster in connections than 5G, allowing users to upload and download various applications such as streaming and gaming more easily. |
| Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR) | 6G has potential capabilities to revolutionize AR and VR with its ultra-low latency and high speed, expanding applications such as gaming, education, training, and entertainment. |
| Internet of Things (IoT) | 6G networks are expected to handle a vast number of connected devices simultaneously, enabling the next level of integration for smart homes, industrial IoT, smart cities, and environmental monitoring. |
| Autonomous Vehicles | Autonomous vehicles can relay information internally and with the outside environment using 6G technologies, improving safety and efficiency on the roads. |
| Healthcare | 6G could facilitate remote patient monitoring, consultations, and surgeries with unprecedented accuracy and responsiveness, transforming healthcare delivery. |
| Advanced Manufacturing | 6G could optimize the manufacturing process by assisting in real-time monitoring and control, enhancing efficiency and improving process execution. |
| Environmental Monitoring | 6G could play a key role in environmental applications due to the increased number of connected devices and sensors, making data collection and analysis more effective. |
When is the anticipated arrival of 6G?
As of now, 5G technology is still being rolled out globally and standardized. This ongoing deployment phase suggests that it will take some time before 6th generation technology becomes a reality. Nonetheless, the opportunities, applications, and potential technologies of 6G networks are already being considered by scholars, technology firms, and telecom organizations. Even if there is no clear timeline in which it will come to pass, some estimates indicate that the 6G internet may be available for commercial reach by around 2030-2035.
This timeline is supported by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers, a non profit society on technology standardization through its journal “6G Architecture to Connect the Worlds” published in the domain of this Association’s structure.6G Architecture to Connect the Worlds. According to the paper, “2030 and beyond will present unique challenges and opportunities of global relevance and scale. We need an ambitious 6G vision for the communications architecture of the post-pandemic future to enable growth, sustainability, and full digital inclusion.”
In 2020, serious research and development efforts for 6G technology began, with initiatives such as the 6G Flagship in Europe and Japan’s $482 million commitment to 6G expansion by 2025. In Russia, institutions predict 6G network availability by 2035. American mobile providers like AT&T, Verizon, and T-Mobile are also advancing their 6G innovation roadmaps through initiatives like the Next G Alliance, which started developing 6G technology in May 2021.
Who is working on 6G technology?
Several companies and research institutions are actively involved in developing 6G technology. While the specifics of their projects and contributions may vary, here are some notable entities working on 6G:
| Notable Entities Working on 6G | Description |
|---|---|
| University of Oulu's 6Genesis Program | Based in Finland, the 6Genesis program collaborates with industry partners, academic institutions, and government agencies to drive innovation in wireless communication technologies for 6G networks. |
| Osaka University in Japan | Osaka University and Adelaide University have collaborated to create a silicon-based multiplexer to simplify the transmission process in 6G networks. |
| Huawei | The Chinese telecommunications giant is investing in terahertz communications and artificial intelligence for 6G technology development. |
| Samsung | Samsung is exploring ultra-high-frequency bands and advanced antenna technologies for 6G research and development. |
| Nokia | Nokia is conducting research into advanced wireless communication techniques, network architecture, and spectrum usage for 6G technology. |
| Ericsson | Ericsson is focusing on terahertz communications, massive MIMO technology, and AI for network optimization in its 6G R&D efforts. |
| NTT Docomo | The Japanese telecommunications company is exploring new communication paradigms, advanced antenna technologies, and network architectures for 6G. |
| Intel | Intel is investing in terahertz communication, advanced chip technologies, and AI for wireless networks in its 6G R&D. |
| Qualcomm | Qualcomm is working on advanced semiconductor solutions, mmWave communication, and AI-driven network optimization for 6G. |
| Apple | Though not officially confirmed, there are reports suggesting that Apple is exploring 6G technology and investing in related research and development. |
Difference Between 6G & Another G Network
With each new generation of technology, our focus changes. 2G and 3G were about talking and texting. 4G brought lots of data, and 5G connected things like smart devices. In the future, with 6G, everything will blend – the digital, physical, and human worlds. Smart systems will make us more efficient and change how we live and work.
Mobile Generations
| Feature | Release Year | Data Speed |
|---|---|---|
| 1G | 1980s | Kbps |
| 2G | 1990s | Kbps |
| 3G | Early 2000s | Mbps |
| 4G (LTE) | 2010s | Mbps/Gbps |
| 5G | 2020s | Gbps |
| 6G (Expected) | Anticipated 2030s | Tbps |
What are the challenges of 6G network technology?
6G network technology faces several challenges as it moves toward development and deployment:
1. Technological Limitations:
Developing 6G technology requires overcoming significant technological hurdles, such as achieving reliable communication in the terahertz frequency range and addressing the complexities of integrating advanced features like holographic communication and quantum networking.
2. Spectrum Availability:
Securing the necessary spectrum for 6G networks, especially in the terahertz frequency bands, poses a challenge due to regulatory and technical considerations. These frequency bands require careful management to avoid interference and ensure efficient spectrum utilization.
3. Infrastructure Requirements:
Implementing 6G networks will require substantial infrastructure upgrades, including the deployment of new base stations, antennas, and backhaul networks capable of supporting the increased data rates and low-latency requirements of 6G.
4. Energy Efficiency:
Achieving energy-efficient operation is crucial for 6G networks, especially as data rates and network complexity increase. Optimizing energy consumption across network components while maintaining performance will be a significant challenge for researchers and engineers.
5. Security and Privacy:
As with any wireless technology, ensuring the security and privacy of user data and network communications is essential for 6G networks. Addressing potential vulnerabilities and designing robust security mechanisms to protect against cyber threats will be a priority during the development of 6G technology.
6. Global Standardization:
Developing global standards for 6G technology is critical to ensuring interoperability, compatibility, and seamless connectivity across different networks and devices. Achieving consensus among industry stakeholders and regulatory bodies on standardization issues will require extensive collaboration and coordination.
7. Cost and Affordability:
Deploying 6G networks involves significant investments in research, development, and infrastructure deployment. Balancing the costs of developing and implementing 6G technology with the affordability of services for end-users will be a key consideration for industry stakeholders and policymakers.
Conclusion - 6G
As technology continues to evolve, 6G networks stand as a beacon of innovation, promising unprecedented speed, connectivity, and capabilities that have the potential to reshape industries, enable new applications, and empower societies in ways we can only begin to imagine. While the full realization of 6G may be years away, it serves as a reminder that the relentless pursuit of faster, more efficient, and more connected networks remains at the heart of our digital future. Keep a watchful eye on the horizon, for 6G may well be the bridge to a new era of connectivity and possibilities.
Frequently Asked Questions: Sixth Generation
As of March 2024, having 6G Wi-Fi in your home is highly unlikely. 6G technology is still in the early development stages and won't be widely available for several years. Additionally, most devices, like phones and laptops, aren't compatible with 6G frequencies yet, as they are designed for certain 5G frequencies. Until 6G becomes widely accessible and devices are compatible, having 6G in your home is improbable for now.
It's challenging to pinpoint an exact timeline for when we'll see 6G products, but it's unlikely to happen anytime soon. Currently, we're still in the early stages of developing and deploying 5G networks globally, and 6G technology is still in the research and development phase.
China recently launched a 6G satellite as part of its efforts to advance the development of 6G technology.
China aims to stay at the forefront of wireless communication technology by investing in 6G research and infrastructure. This initiative underscores China's commitment to innovation and leadership in the global telecommunications industry.
The satellite is intended to provide a platform for research and experimentation to improve the engineering, manufacturing, and prototyping of 6G devices.
The satellite launch signifies China's dedication to laying the groundwork for future innovations in wireless communication. By investing in 6G technology now, China seeks to position itself as a leader in the development and deployment of next-generation wireless networks and technologies.
6G technology is expected to offer significantly faster speeds, lower latency, and greater capacity compared to current wireless standards. It could enable transformative applications in areas such as healthcare, transportation, and entertainment.
While the launch of China's 6G satellite is a significant step, widespread adoption of 6G technology may still be several years away. The timeline for 6G deployment will depend on factors such as technological advancements, regulatory considerations, and market demand.
6G technology promises faster speeds, lower latency, and greater capacity, allowing for quicker downloads, smoother streaming, and improved gaming experiences. It enables near-instantaneous communication, supports more connected devices, and fosters innovative applications like advanced healthcare solutions and immersive virtual experiences. With 6G, you can expect enhanced global connectivity and improved access to information and services, transforming the way we communicate and interact with technology.