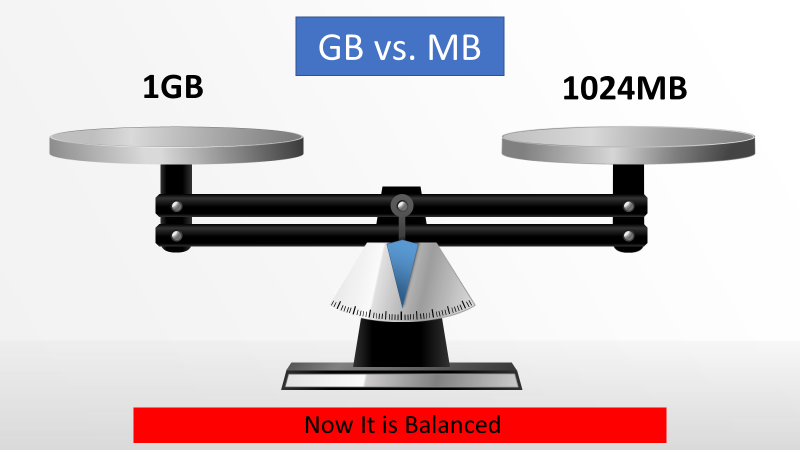
A GB stands for a Gigabyte and it is a bigger storage unit as compared to an MB short for a Megabyte. For one, one gigabyte comprises 1,024 megabytes. This means, therefore, one GB accommodates 1,024 MB.
At present, where almost everything can be virtualized and there exists an auxiliary virtual space, it is worth knowing how much is 1 megabyte (MB) and 1 gigabyte (GB). When installing a program on the computer, want to copy files, stream videos from the internet or any other activity involving data.
Of course! Although most people grasp with no troubles the fact that gigabytes (GB) is larger in size than a Megabyte (MB), as to what extent this difference is and the difference between the two sometimes baffles most.
Through this in-depth guide, we shall explain MB as a measuring unit, mode of measuring MB against GB and why there is a need to know about MB and GB in computing.
How Many MB in a GB?
Let us take a look at a quick comparison and how many MB in a GB with the simplest formula
Below is the formula that expresses how to change the gigabytes to megabytes:
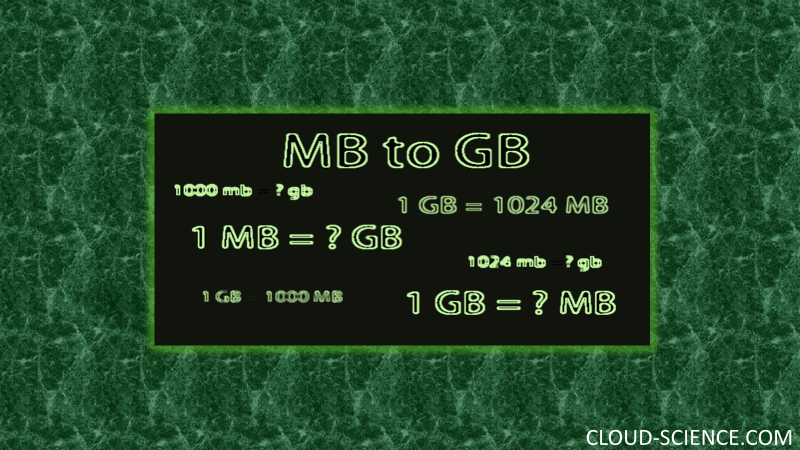
1 GB =1000 MB (Decimal system used by manufacturers)
1GB =1024 MB (Binary system used in computer operating)
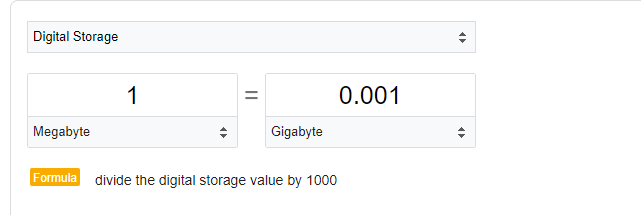
Conversion Formula: MB into GB
Number of Megabytes (MB)=Number of Gigabytes (GB)/1000
MB vs GB: A Quick Comparison Table
Let’s take a look at Quick comparison.
| Measurement | Megabyte (MB) | Gigabyte (GB) |
|---|---|---|
| Decimal | 1 MB = 1,000 KB | 1 GB = 1,000 MB |
| Binary | 1 MB = 1,024 KB | 1 GB = 1,024 MB |
| Bytes | 1,048,576 bytes (1 MB) | 1,073,741,824 bytes (1 GB) |
| Symbols | MB, MiB | GB, GiB |
| Follows | Kilobyte | Megabyte |
| Followed By | Gigabyte | Terabyte |
| Usage | Smaller storage: Documents, images, music files | Larger storage: Hard drives, memory cards |
Megabyte (MB) vs Gigabyte (GB): What’s the Difference?
The data comparative above provides us a very good grounds for determining what has been the level of bettering in the storage space playing field between the megabyte (MB) as compared to the gigabyte (GB). Furthermore, let us further elaborate and explain the characteristics of each one of them also the interplay between them.
Megabyte and gigabyte are appropriate factors of measuring the capacity of a computer, like the volume is expressed in liters or gallons with regard to liquids. The content one gigabyte of electronic storage is easier to explain when relating it to several megabytes; a megabyte (MB) is a smaller unit of measurement and is equivalent to almost a million bytes. It typically measures smaller files like documents, images, or short videos
In contrast, one gigabyte (GB) is of a larger magnitude: it is approximately the size of one billion bytes which can be taken as around ‘one truncated zero’ more than the megabyte. Gigabytes are commonly used to quantify larger files such as high-resolution videos, extensive software applications, or large collections of photos.
To put it simply:
- Megabytes are suitable for measuring smaller amounts of data.
- Gigabytes are reserved for larger amounts of data.
Megabyte vs Gigabyte: Data Storage Compared
Bit, the smallest measure of storage in computing, is a binary digit which may represent any one number-0 or 1 which refers to two electric ‘off’ and ‘on’ states respectively. Since bits are of minimal size, it’s uncommon to handle information individually at the bit level. Typically, bits are grouped into sets of eight to create a byte.
The common understanding that a kilobyte is equal to one thousand bytes is quite misplaced because a kilobyte is in fact 1024 bytes. The reason for this is of course the computational society being in the binary designation as opposed to the decimal.
The information size of a computer is often described in kilobytes, megabytes, gigabytes, and terabytes. These units assist in measuring the amount of data that can be stored, sent or processed in the systems.
- Kilobytes (KB):
- The smallest commonly used unit.
- Equivalent to 1,024 bytes.
- Often used to measure small files like text documents, simple images, or short audio clips.
- Megabytes (MB):
- One step up from kilobytes.
- Equal to 1,024 kilobytes or approximately 1 million bytes.
- Frequently used to measure larger files such as photos, songs, videos, or documents with images.
- Gigabytes (GB):
- Significantly more extensive than a megabyte.
- Encompassing 1,024 megabytes or roughly 1 billion bytes.
- It is commonly used to measure the storage capacities of devices like hard drives, SSDs, or memory cards, as well as the size of large files such as high-definition videos, software applications, or databases.
- Terabytes (TB):
- Even larger units.
- Representing 1,024 gigabytes or approximately 1 trillion bytes.
- Used to measure extensive data storage capacities, such as enterprise-level servers, cloud storage solutions, or massive multimedia libraries.
Important information
Every higher category is increased by a factor of 1,024 over the previous category.
Take for example a hard disk drive as branded by the manufacturer with the standard decimal values of 100 Gigabytes. In this system, one Gigabyte is taken to be one billion bytes. On the other hand, your computer uses the binary system; that is, it counts in powers of two. Thus, the same hard disk, in one of its definitions, is said to hold approximately 107,374,182,400 bytes approximately. That’s why a car, for example, that possesses such a hard disk, while comforted by the HD random access disk label, which is generally within its range, might show a performance lower than the maximum capacity etched the hard disk casing.
For example, instead if it displays 100 GB, it may probably be about 93.13 instead. This difference is within the normal range and does not mean that something is wrong with the computer, it is just one of the fakes in the storage, the standards used for its measure are different.
When should we use megabytes MB or gigabytes GB and which one?
Coming to megabytes MB and gigabytes GB, the deciding factor is the amount of data in consideration and the reason for usage. Here are the instances when it is right to use each
1. Megabytes (MB):
Use megabytes when you’re dealing with smaller amounts of data. For example:
- Sharing a single photo or document with a friend.
- Downloading a short song or video clip.
- Checking the size of a small app or file on your computer.
2. Gigabytes (GB):
Use gigabytes when you’re dealing with more significant amounts of data. For instance:
- Storing an extensive collection of photos, videos, or music on your computer or phone.
- Downloading or streaming full-length movies or TV shows.
- Checking the storage capacity of a hard drive, USB flash drive, or smartphone.
What are the bigger units than MB and GB?
Here’s an explanation of each of those alternative units of data storage:
| Unit | Equivalent | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Terabyte (TB) | 1,024 GB | Often used for large data storage like external hard drives, servers, and cloud storage |
| Petabyte (PB) | 1,024 TB | Commonly used for massive data sets in data centers and supercomputers |
| Exabyte (EB) | 1,024 PB | Describes huge data storage capacities, seen in global data networks and large-scale scientific research |
| Zettabyte (ZB) | 1,024 EB | Quantifies vast amounts of data generated by the modern digital world, including data from IoT devices and big data analytics |
| Yottabyte (YB) | 1,024 ZB | Represents an almost inconceivable amount of data storage, typically used in theoretical discussions |
Conclusion:
The very definition of computing says that the difference of whether the torrents are in mb or gb and so on, is of paramount importance and needs to be taken into consideration of data management. It does not matter whether it be an attachment in an email, the size of a hard drive or the demands of video content, knowing the difference between MB and GB is very important. It is undoubted that unlike the earlier years when advanced applications were scarce, the current world is filled with the longing for such applications enabling more and more people to be collecting large amounts of data.
FAQs: MB vs GB
No, Megabytes and Gigabytes represent significantly different levels of data storage. Using them interchangeably can lead to misunderstandings regarding file sizes and storage capacities.
As per binary computer operation language, there are approximately 1,024 megabytes in a gigabyte and 1000 megabytes per manufacturing style.
A yottabyte is the most significant unit recognized by the International System of Units (SI). It's massive, containing around 1 septillion bytes. In simple terms, that's written as 1 followed by 24 zeros: 1,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000 bytes. To grasp its enormity, consider it equal to a quadrillion gigabytes (GB) or a million trillion megabytes.
No, digital storage is measured in smaller units like kilobytes (KB) and larger units like terabytes (TB), petabytes (PB), and exabytes (EB).
When selecting a storage device, factors include storage capacity, speed, durability, compatibility with your devices, and backup options.